When someone reads about the Go programming language, they would probably come across Rob Pike’s famous ‘Concurrency Is Not Parallelism’ talk or they might discover that Docker and Kubernetes and many other cloud infra tools have been written in Go (Go has been dubbed ‘The Language of the Cloud’). I want to write about one of Go’s lesser known tool in the box - Gomobile. Gomobile is a mobile application development tool written in Go, built with the aim of developing cross-platform applications.
Why would you try Gomobile?
I can hear your collective groan, ‘Not another Cross Platform Mobile Development Solution’. And I agree, and infact I would want to lend my voice to it. Sometimes the benefit of having a single codebase pales in comparison to the sub par experience provided by cross platform frameworks.
So why are we talking about Gomobile then?
Gomobile provides two strategies for development
-
To develop an entire mobile application using -
gomobile build -
To develop a library that can be used by mobile applications using -
gomobile bind
Using Gomobile as a generator for SDKs that can be plugged into applications is very similar to how companies are Google and Dropbox are approaching cross-platform development. Google used J2OBJC in Inbox
and Dropbox has Djinni.
gomobile bind is an option if your application has a lot of business logic that you don’t want to rewrite in multiple platforms.
Gomobile bind
gomobile bind generates language bindings for Java and Objective-C. A simple pattern for developing mobile applications using bind would be develop the view layer in the native language and then communicate with the generated sdk to obtain model objects.
Mobile App Architecture
There are quite a few mobile application architecture patterns in Android and iOS like MVC, MVP, MVVM, and VIPER. All of these architectural designs can be broadly represented by three layers.
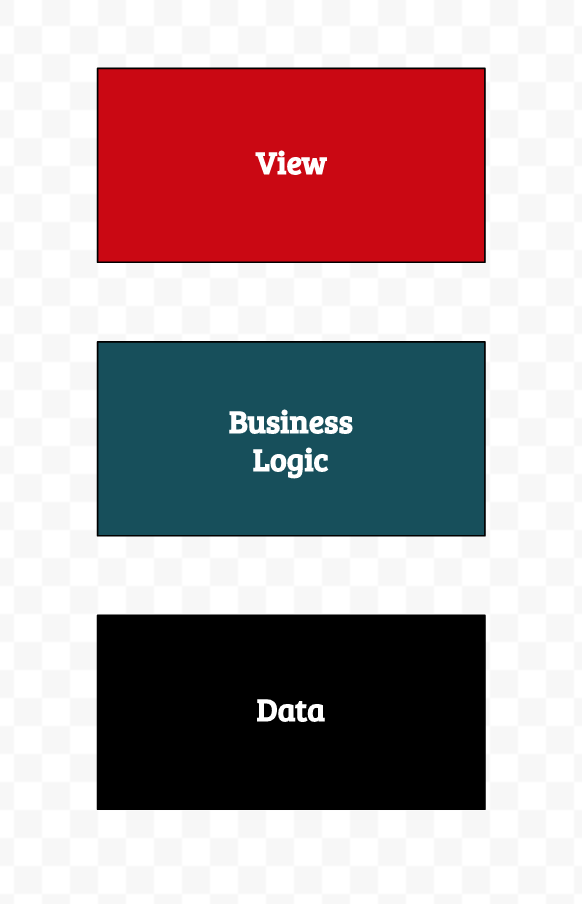
View Layer
This layer is responsible for user interaction and rendering of data. Activity and ViewController classes in Android and iOS respectively are types of classes that are normally associated with this layer.
Business Logic Layer
This layer contains the core application logic. The interactions from the view are sent to this layer, which is processed and used to make calls to the data layer.
Data Layer
The data layer controls all of the data access operations. This can be anything from accessing a local SQLite database to interacting with the network.
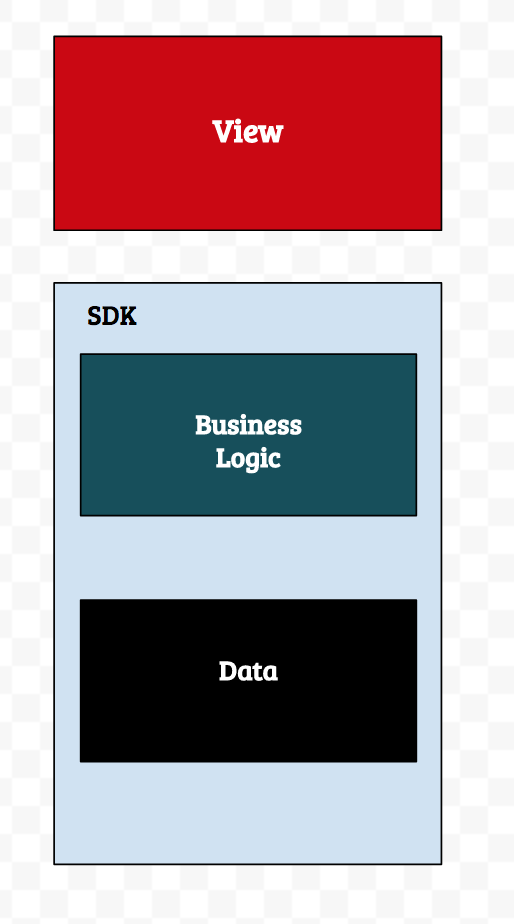
With gomobile bind, the business logic and data layers can be moved to Go and shared between iOS and Android applications. This way business logic needs to be written only once and the data access protocols are similar between operating systems. You also don’t lose out on the user experience which is a common drawback in most cross platform solutions.
References
Here are some references that you might find interesting to get started with Gomobile